Introduction to Hadoop for Data Engineering

Data is growing at an unprecedented rate, and traditional systems are struggling to keep up with it. To manage this growing data, new technologies have emerged, and Hadoop is one of the most popular technologies today. Hadoop is an open-source framework that allows distributed processing of large datasets across clusters of computers using simple programming models. It is widely used for big data storage, processing, and analysis. In this blog post, we will explore what Hadoop is, its components, and how it works.
What is Apache Hadoop?
Hadoop was developed by Doug Cutting and Mike Cafarella in 2006, and it is a part of the Apache project managed by the Apache Software Foundation. Hadoop is an open-source distributed computing framework used for storing and processing big data. It is designed to store and process large datasets across a cluster of machines, using simple programming models. Hadoop has two main components: the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and MapReduce. Hadoop allows developers to write complex MapReduce programs that can process large datasets in parallel across a large number of nodes.
Hadoop Components
As mentioned before, Hadoop consists of two major components: the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and MapReduce. Let's dive into each component in more detail.
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
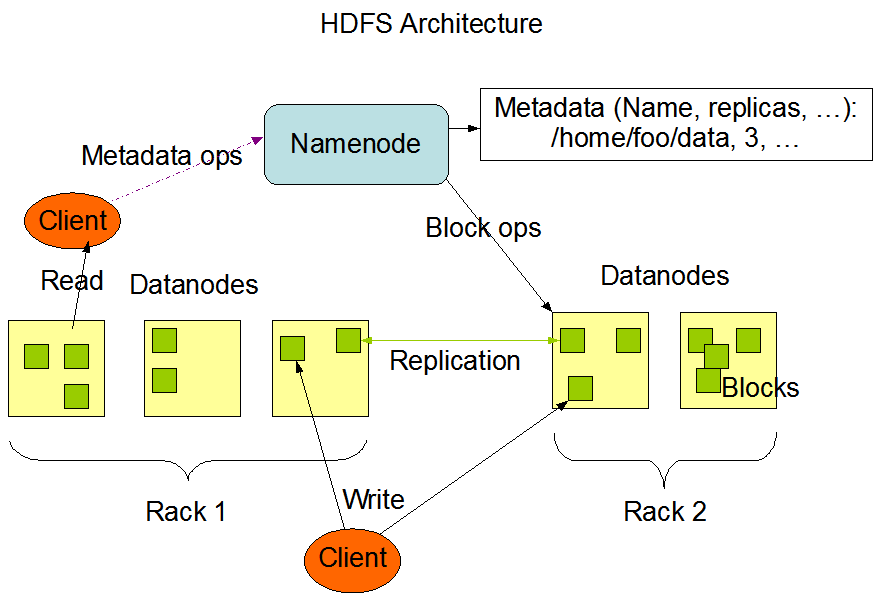
HDFS is a distributed file system designed to store large data sets reliably and fault-tolerantly. It is modeled after the Google File System (GFS) and provides scalable and fault-tolerant storage for big data. HDFS is designed to store data across a large number of machines and to provide transparent access to the data for applications. The data is split into blocks and distributed across the nodes in the cluster. Each block is replicated across multiple nodes to provide reliability and fault tolerance. HDFS also provides data locality, which means that the MapReduce tasks are executed on the node where the data is located, reducing network traffic and improving performance.
MapReduce
MapReduce is a programming model for processing large data sets in a distributed and parallel manner. It is inspired by the map and reduce functions in functional programming. MapReduce is a parallel processing model that breaks down large datasets into smaller, more manageable ones, and then processes them in parallel across a large number of nodes. Each node performs a Map operation, which takes the input data and converts it into a key/value pair. The results are then sorted and shuffled across nodes to group together all the values for each key. Finally, a Reduce operation is performed on each group of values to produce the final output. MapReduce is highly scalable, fault-tolerant, and can be used to process and analyze large data sets.
Other Hadoop Components
Hadoop also includes several other components, such as Hadoop Common, YARN, and Hive, which we'll briefly describe below.
- Hadoop Common: This module contains all the common libraries and utilities required by other Hadoop modules.
- YARN: YARN is a resource manager that manages the resources in a Hadoop cluster and schedules the jobs for MapReduce.
- Hive: Hive is a data warehousing and SQL-like querying tool that is built on top of Hadoop.
How Hadoop Works?

Hadoop works by splitting the data into small chunks and then processing it in parallel across a cluster of nodes. The process is broken down into multiple stages, as shown in the figure above.
- Data is first ingested into the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS).
- The MapReduce job is submitted to the YARN resource manager.
- The data is split into small chunks and sent to the nodes in the cluster.
- The Map function is applied to each data record, generating intermediate key-value pairs.
- The intermediate key-value pairs are sorted and shuffled to group together all the values for each key.
- The Reduce function is applied to the groups of values for each key, producing the final output.
- The output is stored in HDFS.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Hadoop is a distributed computing framework used for storing and processing large data sets. It consists of two main components, HDFS and MapReduce, and several other components, such as Hadoop Common, YARN, and Hive. Hadoop works by splitting the data into small chunks and processing it in parallel across a cluster of nodes. Hadoop has become an essential tool for managing big data and is widely used across various industries. With Hadoop, data engineers can store, process, and analyze large data sets efficiently.
Category: Distributed System