Understanding Apache Spark: A Comprehensive Guide for Data Engineers
Apache Spark is an open-source, unified analytics engine that provides an advanced computing framework for large-scale data processing. With its in-memory data processing capabilities, Spark is able to process data quickly and efficiently. In this comprehensive guide, we will cover the fundamental concepts of Spark and show you how to design and implement Spark applications in your data engineering projects.
Understanding Spark
Apache Spark is a distributed computing framework used for big data processing. It provides high-level APIs in Java, Scala, Python, and R, and an optimized engine for distributed data processing with a general-purpose computing approach.
Spark's functionalities can be grouped into several categories, including batch processing, interactive processing, machine learning, stream processing, and graph processing. This means that Spark can handle various data processing tasks in one integrated platform, making it a tool of choice for many data engineers.
Spark Architecture
Spark has three main components:
- The Driver - this component is responsible for coordinating the task distribution and sending instructions to the cluster.
- The Executors - these are worker nodes responsible for carrying out the assigned tasks.
- The Cluster Manager - this component manages the resources and scheduling tasks across the nodes.
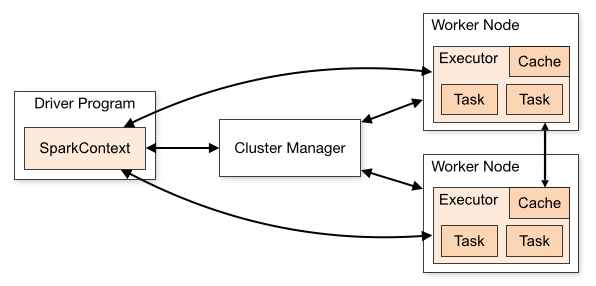
Spark uses a master/slave architecture where the driver program acts as the master and the executor nodes act as slaves.
Spark Core
Spark Core is the foundational computing engine of Spark. It provides functionality for distributed task scheduling, memory management, fault recovery, and data input/output operations. Spark Core also provides a resilient distributed dataset (RDD) abstraction, which serves as the fundamental data structure in Spark.
RDDs are read-only collections of records that can be partitioned across the nodes in a cluster. Each partition of an RDD is processed in parallel, allowing for efficient distributed processing of large datasets. RDDs can be created from various data sources, such as Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), local file systems, and Apache Cassandra.
Spark SQL
Spark SQL provides a programming interface for working with structured and semi-structured data using SQL commands. It allows users to intermix SQL queries with Spark programs, making it easy to process structured data in Spark. Spark SQL also provides a DataFrame API, which is an abstraction over RDDs with additional optimizations for structured data.
Spark SQL can be integrated with various data sources, including Hive, HBase, JSON, and JDBC sources. This makes it possible to query data from different sources using SQL commands.
Spark Streaming
Spark Streaming is the stream processing module of Spark. It provides functionality to process real-time data streams in parallel using Spark's core processing engine. Data streams can be ingested through various sources, such as Kafka, Flume, and HDFS.
Spark Streaming processes data streams in small batches, allowing for high-throughput and low-latency processing. It uses a micro-batch processing model, where incoming data is divided into small chunks and processed in parallel across multiple nodes.
Spark MLlib
Spark MLlib is the machine learning component of Spark. It provides scalable implementations of various machine learning algorithms, including classification, regression, clustering, and collaborative filtering. MLlib supports various data sources, including RDDs, DataFrame, and data stored in Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS).
MLlib also provides a higher-level API called ML, which provides an easy-to-use interface for building machine learning pipelines. These pipelines can be used for preprocessing, feature extraction, model training, and prediction.
Conclusion
In this guide, we have covered the fundamental concepts of Apache Spark and its various components. Spark's in-memory computing framework, coupled with its APIs and integration with various data sources, makes it a powerful tool for big data processing. Spark's functionality can be extended further by adding various libraries and packages available in the Spark ecosystem.
Category: Distributed System